|
DEC MMJ serial adapters and cables
DECconnect introductionDEC, Digital Equipment Corporation (now owned by Hewlett Packard) has been a leader in mainframe world for several years. For connection of their systems, they developed a connector system based on modular jacks with 6 leads called DECconnect. The main difference with standard modular jacks is the key which is not in the middle, but at one side. Because of this they are called MMJ for modified modular jack. The shape of the MMJ plug makes it impossible to connect it to regular telephony or LAN networks erroneously. The DECconnect system was not only used for the mainframes, but MMJ sockets also appeared on the DEC Alpha workstations.
MMJ modified modular jack pin assignmentThe six available leads in the DECconnect MMJ connector are used for the main signals in serial communication: Tx and Rx for the data transmission and DSR and DTR for handshaking. In fact, the data and flow control signals are not true RS232 level signals, but RS423 level. The transmit and receive do not have a common ground, but they are differential, i.e. each line has it's relative ground level on a separate lead. By combining both floating minus leads and connecting them to the RS232 signal ground at the other side, signals can in practice be exchanged with a normal RS232 device. For this type of connection DEC sold a number of conversion adapters. For connection of two DTE devices (computers, printers, etc) the BC16E connection cable is available which automatically crosses the pins. Therefore the DEC MMJ system has a well defined way for null modem communication, something which is somewhat problematic with the original RS232 standard.Let us first take a look at the modified modular jack itself. It contains six pins which are symmetric placed to make cross over easy when a flat modular cable with 6 lines is used. In this drawing the key is oriented down and we look at the six leads.
DEC MMJ plug pin assignment 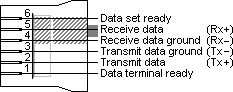 BC16E MMJ crossover cableThe cable used between DECconnect compatible devices is the BC16E which is sold in different lengths. On each side of this cable is an MMJ plug crimped in such a way that the cable effectively works as a cross over cable. The type number is followed by the length of the cable in feet. The BC16E-02 is the part number for the 2 feet version whereas the BCE16E-10 is 10 feet long. Don't be confused by these different part numbers, looking from the communication level they are all the same.
DEC MMJ BC16E crossover cable 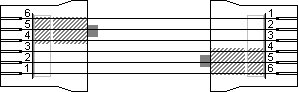
RS232 to DEC MMJ adaptersNow that we have said this about the connection cable, how does an DECconnect MMJ based system connect? For DEC equipment this is easy. Most DEC devices are equipped with a socket which directly accepts the BC16E cable. But also in DEC's glorious time, not only DEC devices had to be connected. Therefore DEC marketed a number of adapters which make it possible to connect the MMJ jacks to a number of devices only equipped with normal RS232 compatible ports. Let's look at them in detail.H8571-J female DB9 RS232 to MMJ adapterFor most of us at this moment the most important MMJ adapter is the adapter to connect a normal PC to a DEC MMJ cable. The original part number for this adapter is H8571-J. This adapter has a female DB9 connector on one side, and a female MMJ socket on the other. The wiring is explained in the diagram.
H8571J adapter, PC RS232 serial port to MMJ 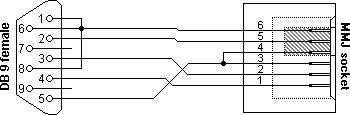
The H8571-J adapter shown here can for example be used to connect a DEC printer with serial MMJ cable to a normal PC RS232 port. Note the connection between pin 1, 6 and 8 in the RS232 connector at the PC side. This connects the printer DTR line through the cross cable BC16E to the PC's DSR, CTS and CD inputs. Some programs need these connections to prevent paper-out and printer off line messages. H8575-A female DB25 RS232 to MMJ adapterNot surprisingly when we look at the era when DEC was at it's glory, there is not only a DB9 version of the RS232 DTE to MMJ converter, but also a DB25 adapter. The part number of this converter is H8575-A and the pin layout is not 100% compatible with her sister. [Both ends of the adapter are female, so I consider it to have female gender red.] The H8575-A was designed for the use with a lot of different DTE type of equipment (terminals, hosts, DEC servers, etc) and not only for PC's like the H8571-J. When looking at the diagram of the H8575-A we see that the RTS and CTS are short circuited at the DTE side where the CTS is connected to the MMJ side on the H8571-J. This loopback increases the amount of MMJ compatible devices: If a RTS/CTS aware device is coupled to the MMJ cabling system, the H8575-A mirrors back the handshaking signal preventing the device from blocking the communication. DTR and DSR must be implemented properly on both sides as this handshake signal is routed through the MMJ cable and not looped back.
H8575A adapter, DTE RS232 serial port to MMJ 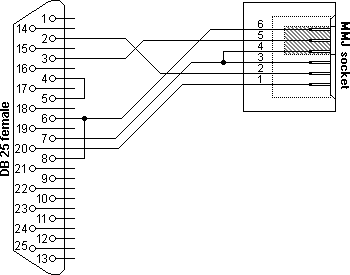
H8575-E male DB25 RS232 to MMJ adapterMost serial printers are equipped with a large sub-D female RS232 connector. Therefore a male db25 to MMJ adapter is necessary to connect most serial printer to a MMJ cabling system. This type of converter bears the part number H8575-E. Wiring is identical to the H8575-A, so we won't discuss the H8575-E adapter here in detail. The wiring diagram is shown below.
H8575E adapter, MMJ to RS232 serial printer 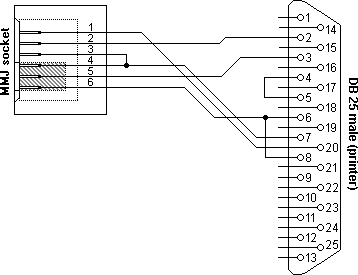
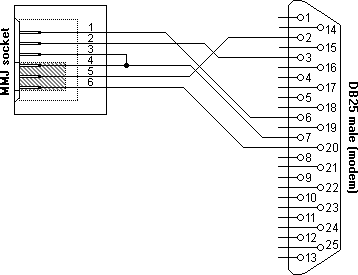
H8571-D and H8575-D male DB25 RS232 modem to MMJ
adaptersAs you might have read
about RS232, the communication standard was mainly developed for
communications between DTE data terminal equipment (computers,
terminals, printers, etc.) and DCE data communication equipment
(modems). Each DTE can be connected to a DCE with a straight through
cable. The communication between two DTE devices with a null
modem is an exception of the rule. DECconnect with it's MMJ based
cabling system is different in such a way that it is primarily developed
for communication between two DTE's directly without use of modems.
Therefore the standard connection cable BC16E is crossed.
If we want to connect a DCE (modem) with this cable, we have to use an
adapter which is internally crossed to neutralize the effect of the
crossover cable. Opposed to standard RS232, with DECconnect connecting
modems is the exception of the rule!
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MMJ socket | DB25 (modem) | Function | With BC16E | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | DTR | DSR | DSR | DTR | DSR | |||
| 2 | 3 | Tx+ | Rx | Rx+ | Tx+ | Rx | |||
| 3 + 4 | 7 | Rx + Tx | Signal ground | Rx +
Tx | |||||
| 5 | 2 | Rx+ | Tx | Tx+ | Rx+ | Tx | |||
| 6 | 20 | DSR | DTR | DTR | DSR | DTR | |||
H8572-00 MMJ to MMJ crossover adapter
There is one child left in the whole DECconnect family. It is the H8572-00 adapter which accepts a BC16E cable at each side. The main purpose is to interconnect cables. The internal wiring of the H8572-00 is identical to the BC16E i.e. it neutralizes the cross links inside the cable.
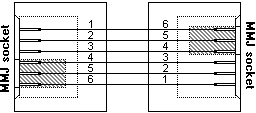
| MMJ socket 1 | MMJ socket 2 | Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | DTR | DSR | |
| 2 | 5 | Tx+ | Rx+ | |
| 3 | 4 | Tx | Rx | |
| 4 | 3 | Rx | Tx | |
| 5 | 2 | Rx+ | Tx+ | |
| 6 | 1 | DSR | DTR | |
Back to ...